Promesse Kayenga
posted on May 20, 2021Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment vs Continuous Integration: Key Definitions
It’s a hot topic of discussion and many books have even been written about this particular subject. In this post, we define each process and we explain how they can all work together so business stakeholders, software developers and project managers alike can work harmoniously in one integrated environment.
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration is the practice of constantly merging development work with a Master/Trunk/Mainline branch so that you can test changes and test that those changes work with other changes. The idea here is to test your code as often as possible so you can catch issues early on. In the continuous integration process, most of the work is done by an automated tests technique which requires a unit test framework. It is best practice to have a build server designed specifically for performing these tests so your development team can continue merging requests even while tests are being performed.
Continuous Delivery
Continuous delivery is the continual delivery of code to an environment once the developer feels the code is ready to ship - this could be UAT, staging or production. The idea behind continuous delivery is that you’re constantly delivering code to a user base, whether it be QA or directly to customers for continual review and inspection. Although similar to continuous integration, continuous delivery differs because it can feed business logic tests where unit tests are unable to catch all business logic, particularly design issues. In this process, you may also be delivering code for code review which may be batched for release or not until after the UAT or QA is done.
The basis of continuous delivery is to have small batches of work continually fed to the next step so it can be consumed more easily and issues can be found early on. This process is typically is easier for developers because issues come to light before the task has left their memory.
Continuous Deployment
Continuous deployment is the deployment or release of code to production as soon as it’s ready. There is no large batching in staging nor a long UAT process before production. Any testing is done prior to merging to the Mainline branch and is performed on production-like environments. The production branch is always stable and ready to be deployed by an automated process. The automated process is key because it should be able to be performed by anyone in a matter of minutes (preferably by the press of a button). After a deploy, logs must be inspected to determine if your key metrics are affected, positively or negatively. Some of these metrics may include revenue, user sign-up, response time or traffic and preferably these metrics are graphed for easy consumption.
The key feature of the continuous deployment process is that it requires continuous integration and continuous delivery because without, you’re guaranteed to get errors in the release.
How They Work Together
Once you’ve moved to a continuous deployment process, you’ll need to have several pieces of automation in place. You must automate your continuous integration build server and continuous delivery to staging, as well as have the ability to automatically deploy to production.
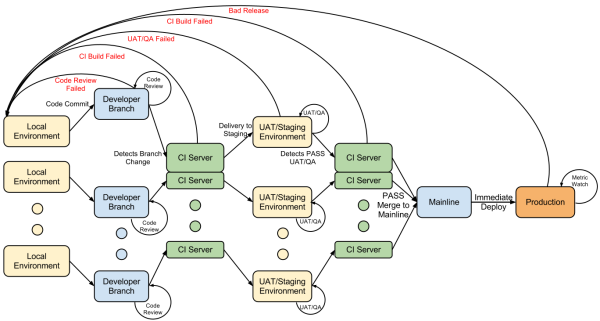
In the ideal workflow, the entire process could be automated from start to finish:
Step 1: Developer checks in code to development branch.
Step 2: Continuous integration server picks up the change, merges it with Master/Trunk/Mainline, performs unit tests and votes on the merge to staging environment based on test results.
Step 3. If Step 2 is successful, developer deploys it to the staging environment and QA tests the environment.
Step 4. If Step 3 passed, you vote to move to production and the continuous integration server picks this up again and determines if it’s ok to merge into production.
Step 5. If Step 4 is successful, it will deploy to production environment.
This process varies slightly based on needs, requirements and approaches.
Continuous deployment relies on small changes which are constantly tested, deployed and released to production immediately upon verification. The ownership of the code from development to release must be controlled by the developer and must be free flowing. The automation of steps allows this process to be implemented and executed without cumbersome workflows.
Key Tools & Best Practices
We at Assembla use the continuous deployment approach and serve many customers that use this approach as well. With the ability to manage tasks and code in one place, Assembla was designed to support this methodology. To help your team run more efficiently, here are key tools we recommend using:
- Jenkins. We love Jenkins here at Assembla. As your team adopts new services, maintaining users and permissions can become difficult to manage. The Assembla Auth plugin for Jenkins enables OAuth authentication for Assembla users to Jenkins instance using your Assembla credentials and delegates the authorization to your project’s space permissions.
- Automated testsuites for the technologies you are using, for example Rspec and Jasmine.
- Version control systems like Git, Subversion or Perforce.
- Desktop Subversion and Git Clients like Cornerstone
- Code reviews like Github pull requests or Assembla merge requests, etc.
- Deployment & staging setup scripts like Capistrano, Shipit, Fabric, etc.
- Integrations with collaboration tools you’re already using like Slack so you can deploy via commands directly in your channel.
Need Help?
Assembla has been around over 10 years helping software development teams launch projects. We have a lot of knowledge in the area of the agile methodology not only because we use it ourselves but we also speak to dozens of teams trying to streamline their workflows, removing inefficiencies that causes project delays.
If you would like to ask us questions specific to your use case, please fill out the form below and we’re happy to help you tackle your project workflow challenges.
